

Discover the untold secrets behind super-thin injection molded parts, challenging the limits of precision and innovation!
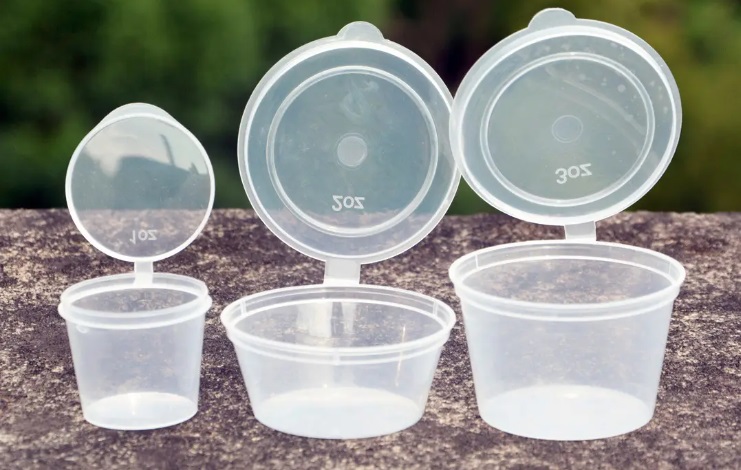

• Understanding Injection Molding and Wall Thickness
• The Art of Precision: How Thin Can Injection Molded Parts Be?
• Challenges in Achieving Thin-Walled Molded Parts
• Benefits of Thin Wall Injection Molding
• Quality Assurance and Maintaining Structural Integrity
• The Future: Innovations and Trends in Thin Wall Injection Molding
Introduction:
Welcome to our blog post where we embark on a fascinating exploration of the world of wall thickness for injection molded parts. Injection molding has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, allowing for the creation of complex and precise components. And at the core of this process lies the determination of the optimal wall thickness. In this curated article, we will delve into the boundaries of thinness, the challenges faced, the benefits reaped, and the impact this has on the overall quality of the molded products.
Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process employed across various industries. It involves the injection of molten material into a mold to create a desired product. Within this process, wall thickness plays a crucial role. Wall thickness refers to the distance between the outer and inner surfaces of the molded component. It is a significant factor influencing part design, performance, and manufacturing costs.
When it comes to wall thickness for injection molded parts, there is a typical range that manufacturers adhere to. However, remarkable advancements have pushed the boundaries of thinness to previously unimaginable levels. Ultra-thin molded components have become a reality, revolutionizing industries and applications.
Design engineers and material experts continuously strive to achieve the thinnest possible walls that still maintain structural integrity. With the aid of modern technology, it is now feasible to manufacture parts with wall thicknesses as low as 0.5mm or even less, depending on the material and design complexity.
From intricate medical devices to fragile electronic components, ultra-thin injection molded parts find applications in a wide range of industries. Their thinness allows for greater design flexibility and efficiency, resulting in lightweight and cost-effective solutions.
Reducing wall thickness comes with its fair share of challenges. Filling the mold uniformly, controlling flow restrictions, and managing cooling are critical hurdles to overcome. When the wall thickness is significantly reduced, the flow of molten material can become restricted, leading to uneven distribution and potential defects. Moreover, rapid cooling of thin sections can cause warping or shrinkage, compromising the dimensional accuracy and stability of the part.
Material selection also plays a vital role in overcoming these challenges. Rigidity, strength, and melt flow characteristics must be carefully considered to ensure the successful production of thin-walled components.
To address these obstacles, advanced manufacturing techniques and tooling systems have been developed. The use of intricate mold designs, hot runners, and specialized cooling systems helps optimize the filling and cooling processes, achieving consistent wall thicknesses and high-quality components.
Thin wall injection molding offers numerous advantages for manufacturers and end-users alike. Some of these benefits include:
Enhanced material efficiency and reduced production costs: Thin walls require less material, resulting in reduced costs and minimized waste. The efficiency gains can have a significant impact, particularly in high-volume production.
Lighter weight and increased fuel efficiency: Thin-walled components are inherently lighter, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as automotive and aerospace industries. Reduced weight contributes to enhanced fuel efficiency and increased payload capacity.
Improved product aesthetics and design flexibility: Thin walls offer greater design freedom, allowing for intricate and sleek product designs. This enables manufacturers to create visually appealing products that stand out in the market.
Efficient heat transfer and better performance: Thin walls provide enhanced thermal conductivity, making them suitable for applications requiring efficient heat transfer. Electronic devices, thermal management systems, and enclosures benefit from this property.
One of the critical aspects of thin wall injection molding is ensuring the structural integrity of the components. Maintaining strength and avoiding defects are paramount to meet the required functional specifications. Sink marks, warpage, and inadequate strength can occur if the thin walls are not handled appropriately.
To ensure high-quality parts, testing and inspection methods are employed throughout the manufacturing process. Advanced simulation techniques, such as Moldflow analysis, aid in predicting potential issues and optimizing the design before production. Quality control measures, including dimensional checks and material testing, play a crucial role in delivering defect-free products.
The race towards thinner walls shows no signs of slowing down. The growing demand for lightweight and cost-effective solutions is driving innovation in thin wall injection molding. Here are some emerging technologies and trends shaping the future:
Micro-injection molding: This technique enables the production of micro-sized components with ultra-thin walls. It finds application in the electronics, medical, and optical industries, among others.
Multi-component injection molding: Combining different materials within a single mold allows for the creation of intricate parts with varying wall thicknesses. This method offers increased design freedom and functionality.
As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in mold design, material selection, and production processes to continue pushing the boundaries of thin wall injection molding. These innovations will unlock new possibilities and applications across various industries, fueling further advancements and enhancing product performance.
The world of injection molding brings forth unparalleled opportunities to create intricate and efficient components. Thin wall injection molding, with its expanding limits, enables lightweight, cost-effective, and aesthetically pleasing solutions across industries. By tackling the challenges associated with ultra-thin walls and maintaining structural integrity, manufacturers can unlock a realm of possibilities while delivering high-quality products. As innovations continue to unfold, the future of injection molding promises to be thinner, lighter, and more remarkable than ever before.






 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  1st Floor, Block1, No.3 Beiting Road, Houting Community, ShaJing Street, Bao'An District, Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province, China
1st Floor, Block1, No.3 Beiting Road, Houting Community, ShaJing Street, Bao'An District, Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province, China